|
Research
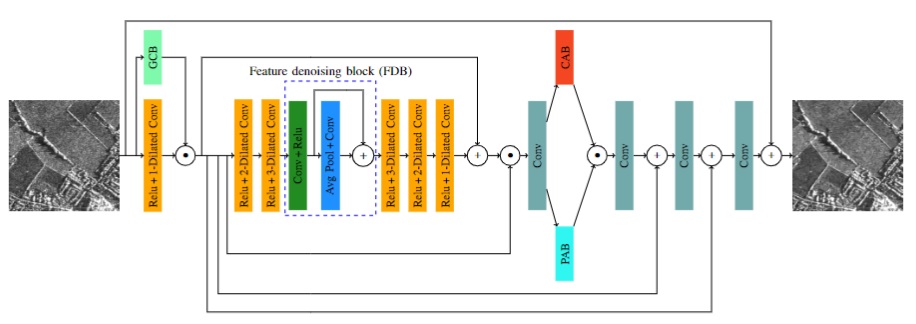 |
AGSDNet: Attention and Gradient-Based SAR Denoising Network
In this work, we propose an attention and gradient-based SAR denoising network (AGSDNet) to remove speckle noise
from SAR images while preserving finer details. In the proposed network, gradient information of the noisy image is
first concatenated with its features in order to increase the feature information content (map). An intermediate feature
denoising block (FDB) is then employed to reduce noise from this feature map. Finally, two attention blocks, designed and deployed,
in the network focus on preserving the more informative features in the image thereby generating a feature preserved denoised
image.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India.
Area of Research - Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Full Text - IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters | IEEE Xplore
|
 |
|
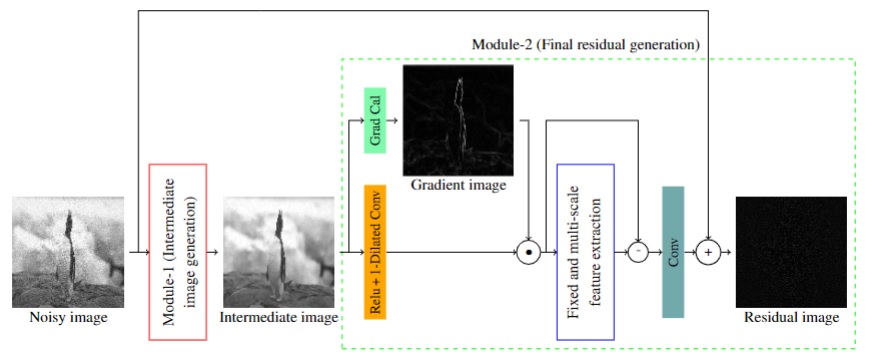 |
Gradient and Multi Scale Feature Inspired Deep Blind Gaussian Denoiser
In this work, a novel deep blind Gaussian denoising network is proposed utilizing the concepts of gradient information,
multi-scale feature information and feature denoising for removing additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) from images. The proposed
network consists of two modules where in the first module generates an intermediate image whose gradient information is
concatenated with the features of second module to generate the final residual image.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India.
Area of Research - Image Processing, Computer Vision.
Full Text - IEEE Access | IEEE Xplore
|
 |
|
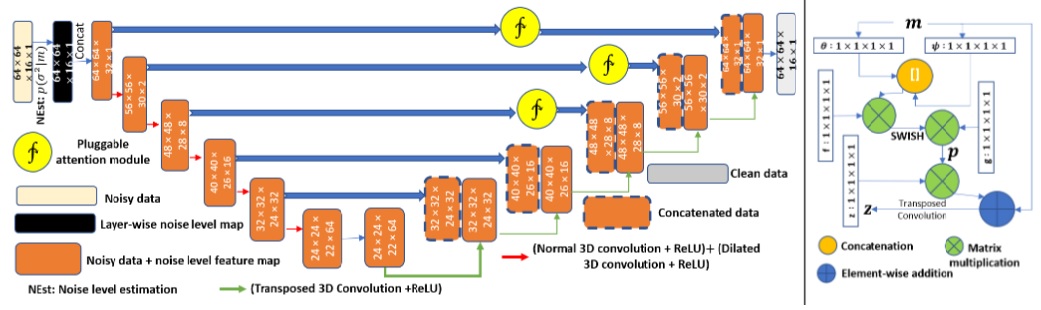 |
Attention-Based Noise Prior Network for Magnetic Resonance Image Denoising
In this work, we propose a novel approach towards denoising MR images using a combination of attention network and noise
level map. The contribution of this work is at three different levels. Firstly Rician noise-level estimation map is fed as
prior along with the noisy input data. Secondly, modified U-Net architecture is used to accommodate non-local multi-level and
multi-scale features. Thirdly, to preserve long-range dependencies in farther symmetric layers, a symmetric-group attention
block is used.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India.
Area of Research - Medical Imaging.
Full Text - IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging ISBI 2022 | IEEE Xplore
|
 |
|
 |
Bayesian Approach in a Learning-Based Hyperspectral Image Denoising Framework
In this work, we design the training paradigm emphasizing the role of loss functions in neural network;
similar to as observed in model-based optimization methods. Further, Bayesian motivated loss functions
also act as priors to constrain the solution space to the types of noise observed in hyperspectral image
acquisition process. As a result, loss functions derived in Bayesian setting and employed in neural network
training boosts the denoising performance.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India, INRIA Bordeaux France.
Area of Research - Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Full Text - IEEE Access | IEEE Xplore |
HAL INRIA | Bibtex
|
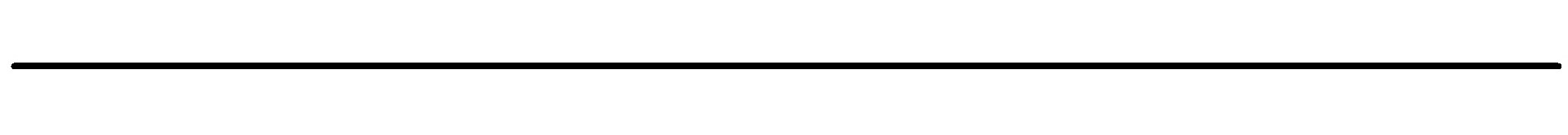 |
|
 |
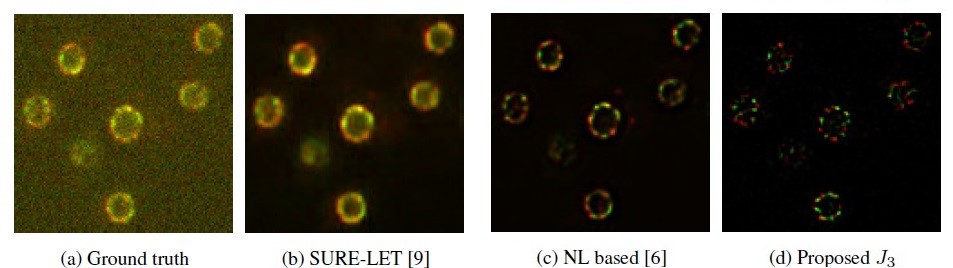
Feature based Denoising for Fluorescence Microscopy
In this work, we propose an image denoising algorithm based on the concept of feature extraction
through multifractal decomposition and then estimate a noise free image from the gradients
restricted to these features. The results obtained have surpassed in quality over the best
algorithms currently available.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India, INRIA Bordeaux France.
Area of Research - Medical Imaging.
Full Text - Scientific Reports | Nature.com |
HAL INRIA | Bibtex
|
 |
Photo-realistic Reconstruction of Camera Images
Camera images are generally limited by the diffraction limit of light, due to which they resultant images
are blurred and noisy. In this work we propose two different techniques for reconstruction of these
noisy images using an optimization based primal dual framework.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India,
MRC Lab of Molecular Biology Cambridge, UK .
Area of Research - Image Processing, Computer Vision.
|
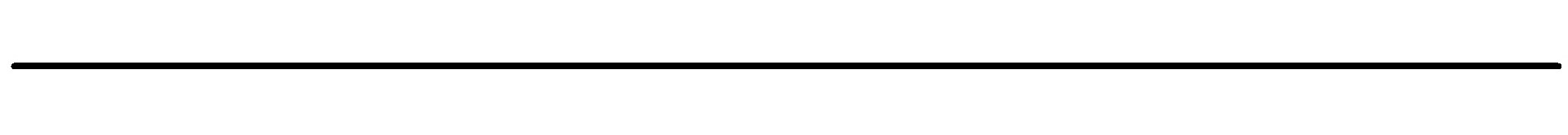 |
|
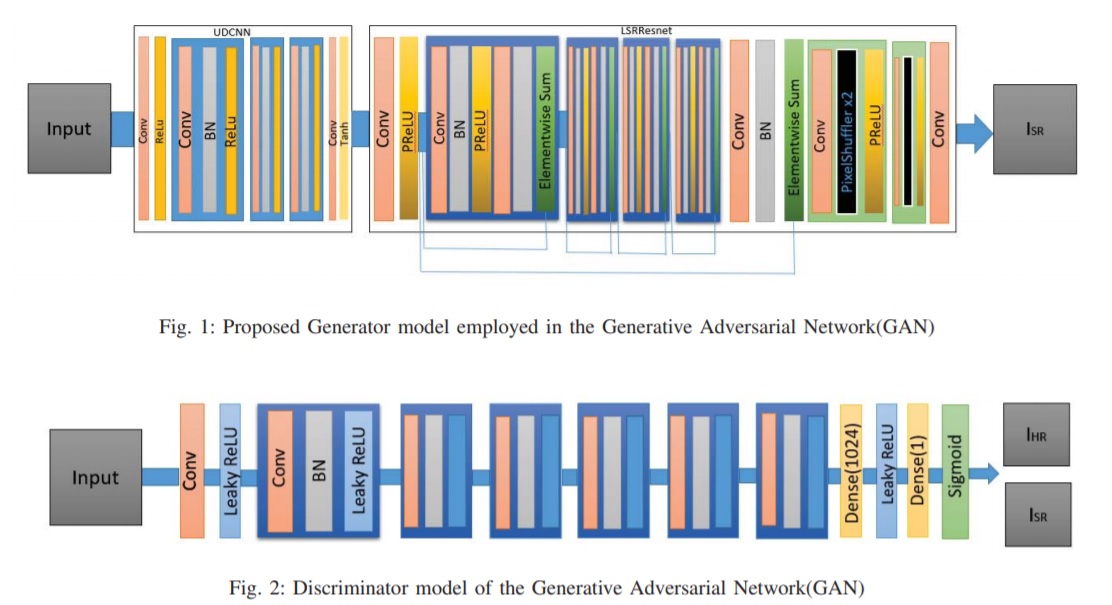 |
Denoised High Resolution Generative Adversarial Network - DHRGAN
The advent of deeper convolutional neural networks and related methodologies have made significant
achievements in the area of single image super-resolution (SISR). However, none
of these techniques are equipped to handle noisy images. In this work, we propose a denoised high
resolution generative
adversarial network (DHRGAN), capable of handling noise
removal from given sample images while trying to super-resolve
it to the desired magnification.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India.
Area of Research - Machine Learning.
Full Text - IEEE Xplore |
Bibtex
|
 |
|
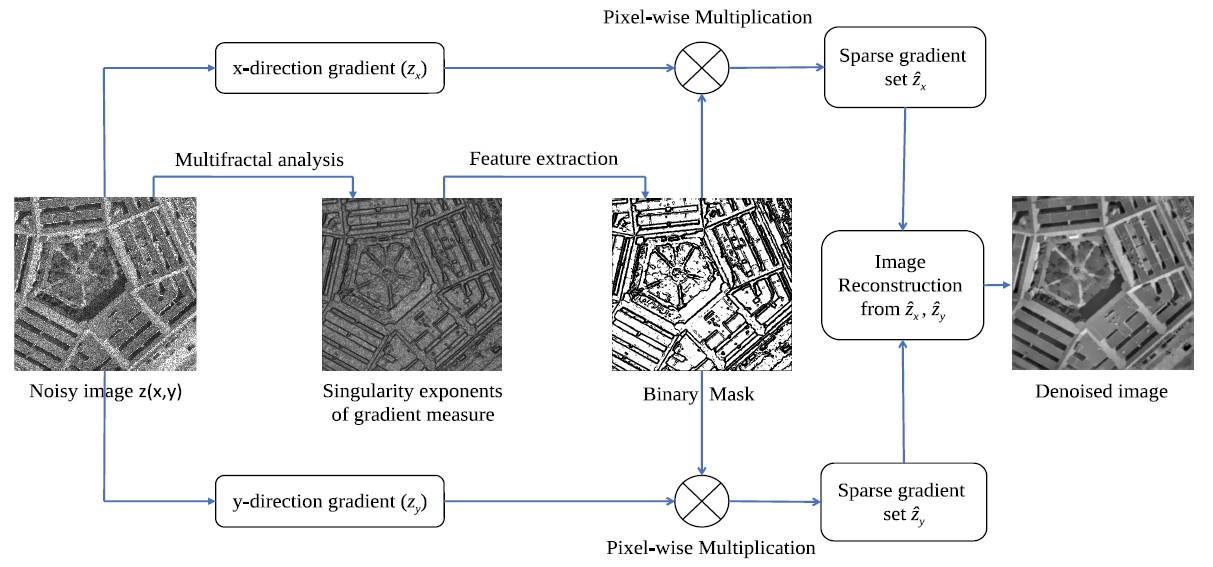 |
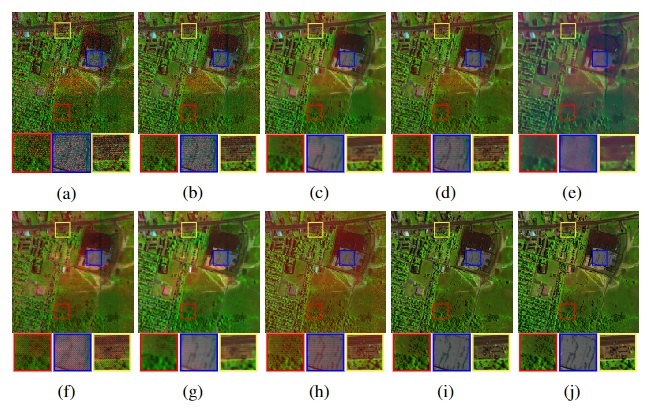
Structure Preserving Denoising of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is a widely used technology for acquiring landscape images
from high altitude reconnaissance aircrafts or low-altitude spacecrafts. The acquired images,
however, suffer from the effect of noise due to random phase fluctuations introduced in the signal
during its acquisition. In this work we propose a noise removal algorithm which also maintains the
texture of the acquired image.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India, INRIA Bordeaux France.
Area of Research - Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Full Text - IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters | IEEE Xplore |
HAL INRIA | Bibtex
|
 |
|
 |
Joint Denoising-Deconvolution Approach for Fluorescence Microscopy
Image denoising and deconvolution are well known techniques applied to wide-field and confocal
microscopy in order to restore images. The methods however suffer from their own drawbacks with
denoising potentially resulting in smoothed images while deconvolution giving unpleasant
artifacts due to ill-posedness of the problem. In this work, we propose to evaluate the interest
of restoring the unknown image through a joint denoising and deconvolution program applied
simultaneously in an iterative framework.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India, INSERM Paris,
Institute Curie, Paris.
Area of Research - Medical Imaging.
Full Text - IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging ISBI 2016 | IEEE Xplore |
Bibtex
|
 |
|
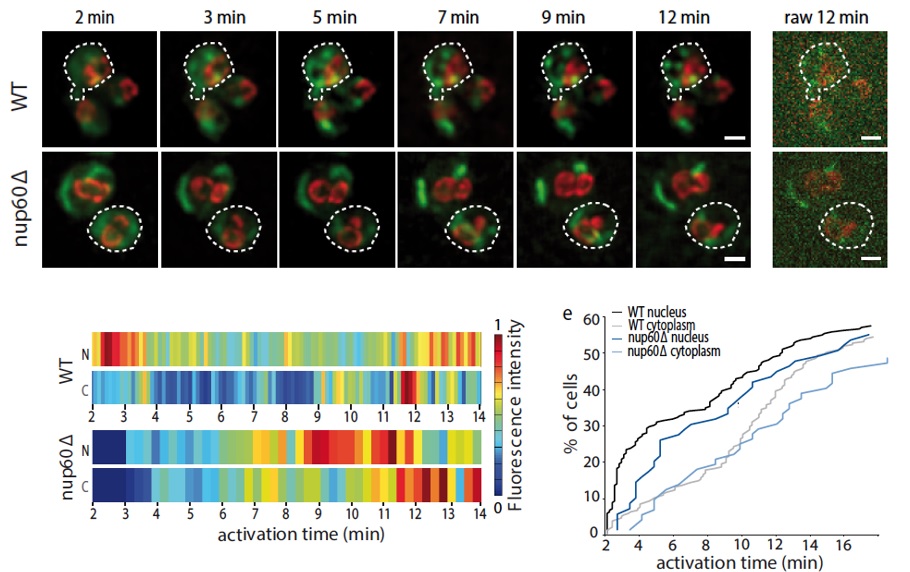 |
Imaging Work-Flow for mRNA tracking in Living Yeast Cells
Objective is to quantify the newly transcribed mRNA
behavior in living yeast cells and correlate transcriptional
dynamics with nuclear pore complex (NPC) function. An adapted spinach-tagged transcript (green) is
used to follow the dynamics of mRNA while the nuclear periphery is defined by tagging
the nucleoporin Nup159 in mCherry (red).
An imaging work-flow is then designed to address the biological questions (mRNA tracking,
gene gating) simultaneously dealing with technical challenges of detecting little molecular
entities and low signal-to-noise (SNR) images.
Participating Organisations - Vanderbuilt School of Medicine USA,
CNRS France, INSERM Paris, Institute Curie, Paris.
Area of Research - Bioinformatics, Medical Imaging.
Full Text - Nature Communications | Nature.com |
PubMed |
Bibtex
|
 |
|
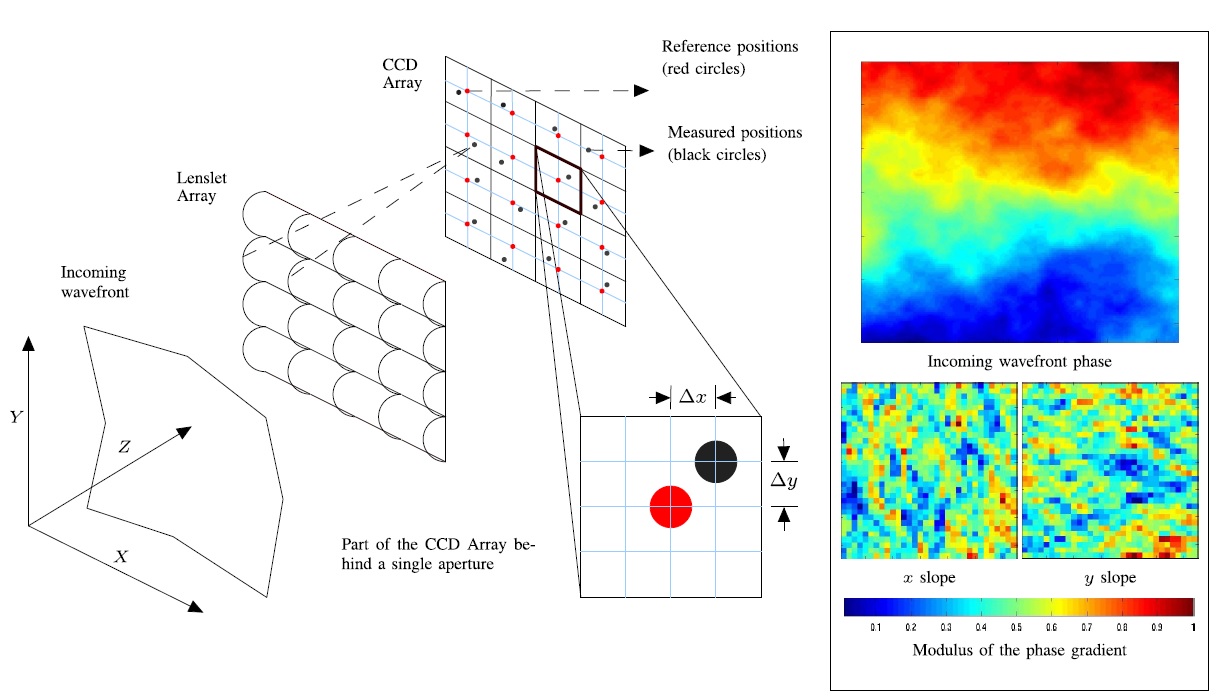 |
Wavefront Phase Estimation Technique for Ground-Based Astronomical Telescopes
Turbulence in the Earth's atmosphere interferes with the propagation of planar wavefronts
from outer space, resulting in a phase-distorted nonplanar wavefront. This phase distortion
is responsible for the refractive blurring of images accounting to the loss in spatial resolution
power of ground-based telescopes. Phase reconstruction from WFS measurements is done by solving
large linear systems, followed by interpolating the low-resolution phase to its desired high
resolution.
Participating Organisations - IIT Patna India, DOTA/E ONERA France,
INRIA Bordeaux France.
Area of Research - Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Full Text - IEEE Transactions in Geoscience and Remote Sensing | IEEE Xplore |
HAL INRIA | Bibtex
|
|